Fusobacterium nucleatum: A Key to Unlocking Colorectal Cancer Insights
A recent review by researchers from California Institute of Behavioral Neurosciences & Psychology meticulously evaluates the influence of gut microbiota on the development and progression of colorectal cancer (CRC), a significant global health concern. Adhering to the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, a thorough database search was conducted, yielding 20 articles that met the inclusion criteria from 2000 to 2023.
Identifying Promising Microbiota Markers for Early Diagnosis and Treatment Enhancement
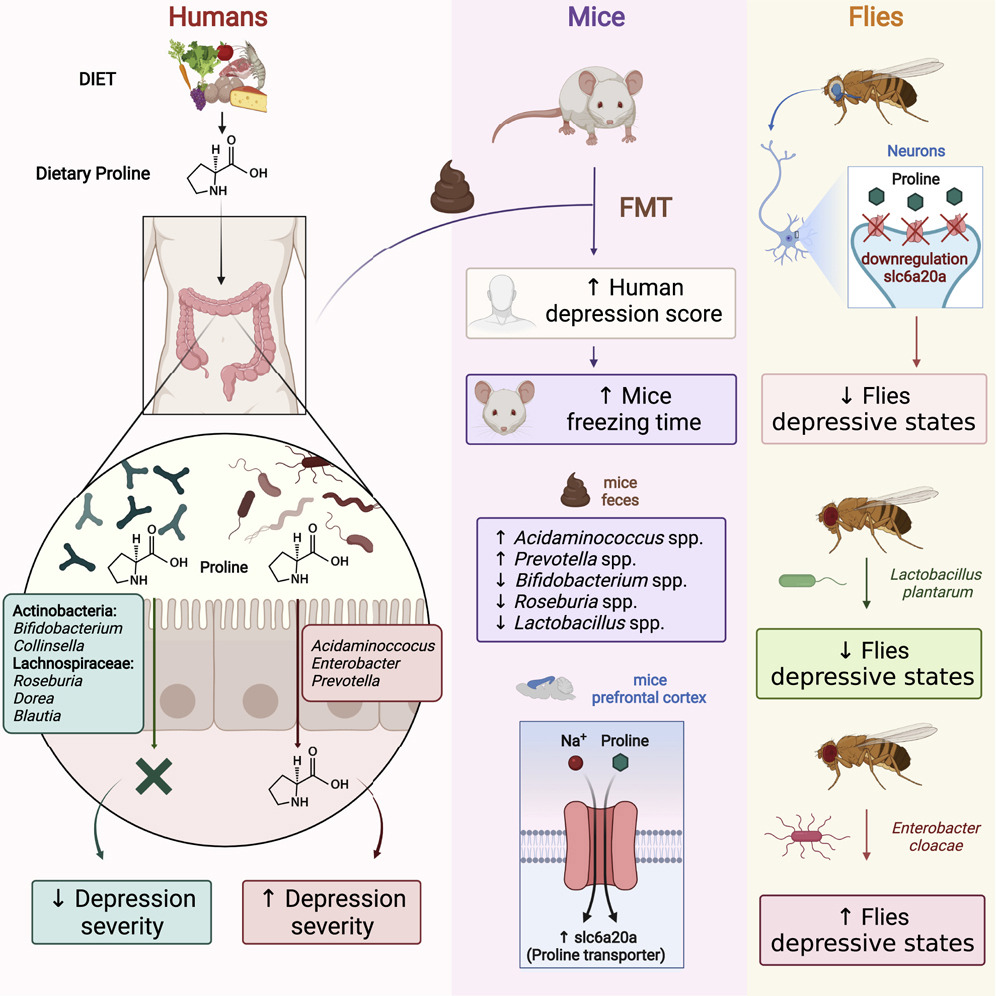
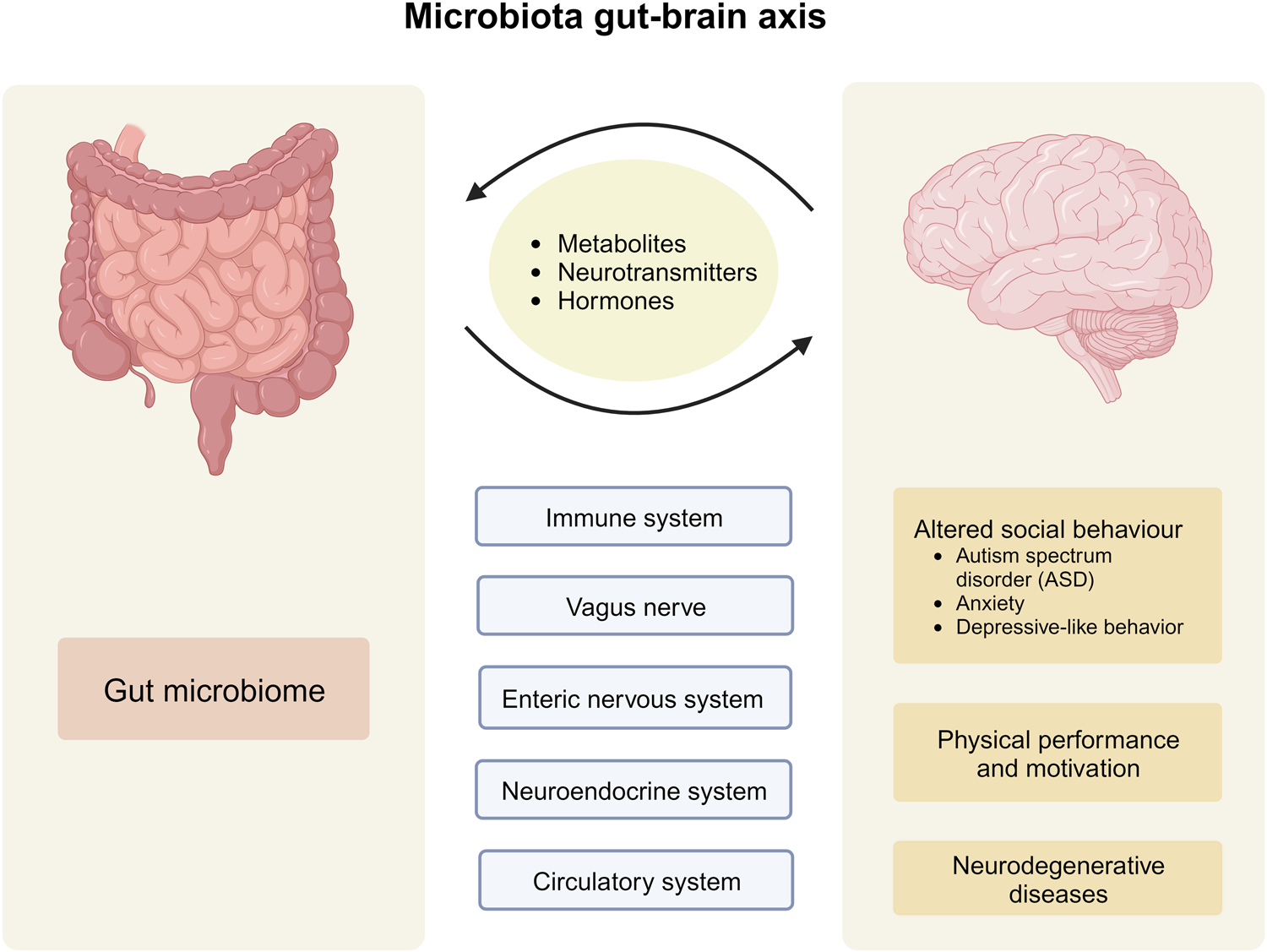
The review highlights the identification of specific microbiota markers, notably Fusobacterium nucleatum, which hold promise for early diagnosis and enhancing treatment of CRC. The synthesis of results underscores a significant correlation between gut and oral microbiota dysbiosis and CRC, suggesting that microbial markers could serve as cost-effective, noninvasive tools for early detection, monitoring recurrence, and evaluating treatment responses.
Addressing Challenges and Calling for Methodological Standardization
However, challenges such as establishing a cause-and-effect relationship, variability in study methodologies, and unaccounted variables like diet and lifestyle present limitations to the current understanding. The review calls for the standardization of microbiota research methodologies to allow for comparable findings across studies and suggests that future research should focus on large-scale multicenter longitudinal studies to validate specific biomarkers for developing universal diagnostic tools.
Exploring Novel Strategies for Prevention and Treatment
Additionally, exploring how microbiota influences CRC pathogenesis could lead to novel prevention and treatment strategies. Despite the low level of study overlap indicating a broad range of unique primary studies and reducing the risk of citation bias, the review acknowledges the need for a deeper understanding of the cause-and-effect relationship between gut microbiota and CRC.
In conclusion, leveraging microbiota markers for CRC could revolutionize early detection and monitoring, but further research is necessary to overcome current challenges and fully harness the potential of microbiome-centered treatments and preventive methods.
Targeting Microbiota 2024 will highlight the latest advancements in microbiome research and different diseases. Don't miss the chance to join the 11th ISM World Congress on October 14-15, 2024 at Corinthia Palace Malta!
Copyright: International Society of Microbiota
Image Credits: Freepik